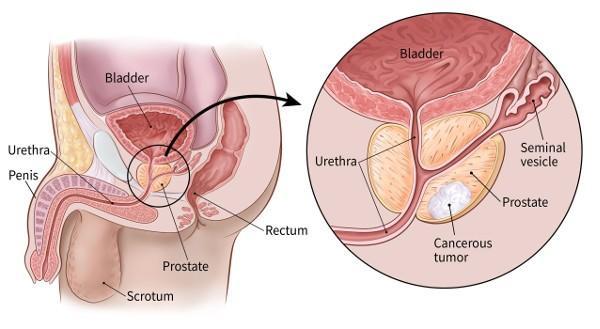
MEDICAL TREATMENT OF THE EPIDIDYMAL CYST
A cyst is a lesion that develops within a tissue or organ. Testicular cysts are benign pathologies that can develop sometimes on the right testicle, sometimes on the left. They particularly affect children and young adults. There are two types of testicular cysts:
Cysts of the epididymis,
Dermoid cysts of the testis.
Cysts of the epididymis are benign tumors of unknown origin. They appear in the form of regular and painless swellings (single or multiple), located at the head of the epididymis.
To permanently cure this disease, Dawasanté experts provide you with a natural treatment based on medicinal plants. Click on the image below to discover this natural treatment.
We deliver all over the world.
For more information, you can contact our experts on +229 51374202 direct line or by WhatsApp at the same number.
The cyst of the epididymis grows at the expense of the swollen part of the upper part or head of the epididymis. There may be one or more cysts within the same epididymis.
The intervention is proposed because of the discomfort or local pain that this cyst can cause. It aims to remove the lesion by the surgical opening of the bursa.
The absence of treatment has no consequence in itself, apart from the fact of a possible increase in the size of the cyst, discomfort, or local pain, which it can cause.
Symptoms and Pains
Concerning the cysts of the epididymis, the manifestations are mainly an increase in the volume of the bursa giving the sensation of having "a ball of fat" at this level, most often accompanied by local discomfort. As for dermoid cysts, the most evocative symptom is the increase in the volume of the bursa. Cysts "rarely cause pain, except in cases of large volume," said Dr. Antoine Faix, surgeon urologist and head of Andrology and Sexual Medicine of the French Urology Association Committee.
The spermatocele kystesdu often contain pools of dead sperm. Doctors don't know what is the cause. Often, epididymal cysts or spermatocele cysts develop for no particular reason.
There are no specific causes for the appearance of a cyst.
Most of the time, cysts in the epididymis don't hurt, so you may not have symptoms. You may only feel a lump when you examine your testicles. Your doctor might find it during an exam. As the cyst gets bigger, you may feel a heaviness in your testicle. You might also notice a lump or swelling behind or above your testicle.
Diagnosis: Who to conduct and what tests to do
If you experience the slightest discomfort and in any doubt, consult your doctor or herbalist quickly, as the symptoms suggesting the presence of testicular cysts are very similar to those suggesting the presence of malignant testicular tumors.
To make a diagnosis on the cysts of the epididymis, it is necessary to do an ultrasound, and possibly a histological examination (sample and tissue analysis) which will reveal the cystic nature of the tumor, and rule out the hypothesis of a cancerous tumor.
The diagnosis of cysts of the epididymis also involves a scrotal ultrasound. This may reveal rounded nodular and cystic formations of varying sizes in the testicular parenchyma (tissue). However, the definitive diagnosis is only established after the histological examination (tissue analysis) which makes it possible to rule out the cancerous hypothesis.
Treatments: What to do if a testicular cyst gets bigger?
Most of the time, this is not the case. Your doctor may prescribe pain relievers to make you more comfortable.
Aspiration is a procedure that can help relieve some of the pain and pressure from the spermatoceles. Your doctor will insert a needle into the cyst to remove some of the fluid.
If the cyst fills up and comes back, your doctor may perform a procedure called sclerotherapy. It will drain some of the fluid from the spermatocele. Then he will use a substance that causes the sac to fill with scar tissue. This tissue could reduce the risk of the spermatocele returning. But it can damage the epididymis. Your doctor can suggest this option only if you are not interested in having children.
In rare cases (if the spermatocele is interfering with your daily life) your doctor may remove it with surgery. It will numb the area, make a small incision (cut) in your scrotum or groin, and remove the growth.
Treatment of epididymal cysts relies on clinical and ultrasound monitoring when the benign cystic nature is evident.
Treatment of an epididymal cyst
The intervention takes place under general or locoregional anesthesia. A short incision is made at the level of the bursa. After checking the underlying testis, the cyst is completely removed by opening the envelope of the epididymis and dissecting as close as possible to the wall of the cyst. Sometimes the surgeon may need to remove part or all of the epididymis.
The intervention is carried out within the framework of an outpatient surgery hospitalization. It may, in some cases, require 1 or 2 days of hospitalization.
Pain at the incision is usually minimal and temporary.
For a few weeks, the bursa remains enlarged and small swelling around the testicle can sometimes persist.
Removal of the epididymal cyst is suggested in the event of an increase in the volume of the bursa and/or any local discomfort or pain associated with its presence. "A short incision is made at the level of the bursa. After checking the underlying testis, the cyst is completely removed by opening the envelope of the epididymis and dissecting as close as possible to the wall of the cyst. The surgeon can sometimes be having to remove part or all of the epididymis ", develops the site of the French Association of Urology. Surgery is also considered in the case of certain dermoid cysts, in the presence of small lesions.
Complicated cases of epididymal cyst
In the majority of cases, the operation takes place without complications. However, any surgical procedure carries a number of risks and complications, which are described below:
Hematoma: bleeding after the operation can lead to the constitution of a hematoma of the bursa, possibly extended to the external genitalia, a reoperation to drain the hematoma may be necessary.
Delayed healing: it may require prolonged local care.
Infection: the existence of discharge through the incision, general signs of infection such as fever, or local signs such as inflammation of the bursa can lead to the initiation of appropriate antibiotic treatment and the treatment of a possible abscess by your surgeon.
Testicular atrophy: it occurs exceptionally after surgery of the epididymis
Recurrence: his risk is extremely low.
Impact on fertility: partial or total removal of the epididymis will permanently prevent the passage of spermatozoa on this side. This risk is rarer in the event of simple removal of the cyst.
Persistence of local discomfort or pain: Removal of the cyst does not guarantee the total disappearance of discomfort or pain.
We deliver all over the world.
For more information, you can contact our experts on +229 51374202 direct line or by WhatsApp at the same number.