PSA AND URINARY INFECTION
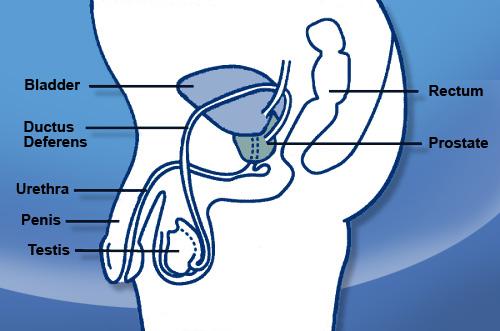
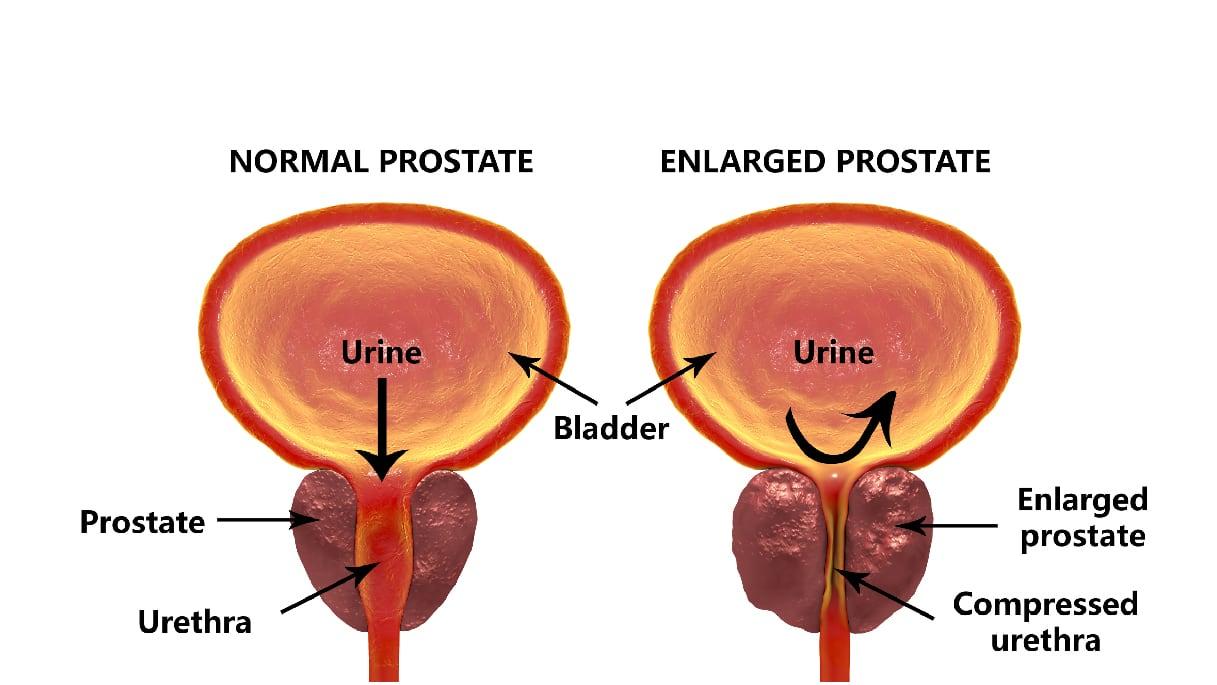
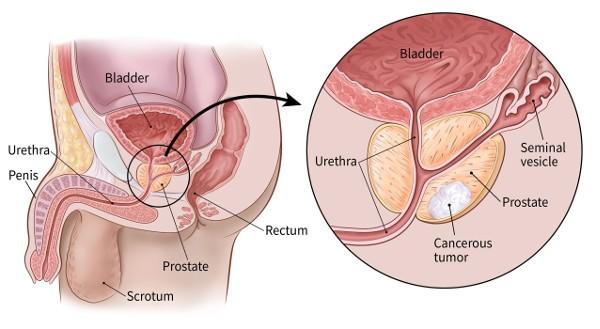
The PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) is a molecule secreted exclusively by the prostate. It plays a role in the liquefaction of semen after ejaculation. It passes into the blood in small concentrations (of the order of one nanogram per ml).
In addition, in humans under 60 years of age, a PSA level of less than 4 ng / mL is considered normal. Beyond this age, and each year, the PSA level increases by 0.04 ng / mL. After 70 years, a PSA level of less than 6.5 ng / mL is considered normal. Discover the natural treatment for prostatitis by clicking on the image below.
We deliver all over the world.
For more information, you can contact our experts on +229 51374202 direct line or by WhatsApp at the same number.
TREATMENT OF INFECTIONS DURING PREGNANCY
A pregnant patient who presents with a urinary tract infection should be treated urgently to avoid an infectious complication with the risk of premature labor or high blood pressure. Many antibiotics are prohibited during pregnancy, and radiological examinations are limited in pregnant women so as not to risk irradiation of the fetus. Choosing the best possible antibiotic depends on the stage of pregnancy, the infectious condition and the possible effects on the fetus.
In case of obstruction of the ureter, the treatment of the infection requires the placement of an internal ureteral catheter until delivery.
URINARY INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN
It is estimated that 3% of girls and 1% of boys have had a urinary tract infection before the age of 11. In children, a urinary tract infection is more often related to an abnormality of the urinary system and additional examinations (ultrasound, intaveinous urography) are often necessary.
In young children, it is sometimes difficult to make the diagnosis of urinary tract infection because the child obviously cannot describe his disorders and the symptoms in children are often atypical and not directly related to the urinary tract: nausea, vomiting, deterioration of the general condition… Sometimes, the occurrence of urinary leaks or bad smell of urine can attract attention.
The symptoms of UTI in children are therefore often unrecognized or attributed to another disease, and UTI should be mentioned when a small child seems nervous, does not eat normally, has a fever. unexplained urine leakage, or any disorder of urinary habits.
In small children, urine collection is usually done through a glued bag.
What are the abnormalities causing urinary tract infection in children?
The abnormalities most often involved in urinary tract infections in children are:
Vesicoureteric reflux:
Normally, urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder, and a valve mechanism prevents urine from flowing back from the bladder to the kidneys. Sometimes this mechanism is incompetent and the urine can go up from the bladder to the ureters and the kidneys, in particular when there is a complete duplication (2 ureters per kidney): this constitutes vesicoureteric reflux. Thus, an infection initially bladder can spread to the kidneys, and give an infection of this one (pyelonephritis). Reflux can also, but more rarely, occur in adulthood.
To check for vesicoureteric reflux, an x-ray is done, called a retrograde cystography. This examination consists of filling the bladder with the radiological products and taking x-rays to highlight possible reflux of the product towards the kidneys.
Congenital obstruction :
A blockage of one or both ureters (megaureter…), or of the urethra can exist congenitally in children (urethral valve…), and can promote urinary infection.
Effects of infections on kidney function:
In children, the risk of damaging the kidney is particularly great if there are infections with vesicoureteric reflux or obstruction of the urinary system. This can lead to scarring on the kidney, poor kidney growth, kidney malfunction with possibly high blood pressure, and rarely kidney failure. If infections are treated early enough and the necessary tests done early enough to treat any serious abnormalities, kidney function can be preserved.
Caused by the tuberculosis bacillus which, after the initial infection of the lungs, migrates to the kidney and/or the prostate. The issue of pus and bacilli in the excretory tract causes symptoms, mainly bladder irritation (frequent urges to urinate, burns when urinating, etc.).
The disease causes strictures of the ureter, a decrease in bladder capacity (small bladder), or even progressive destruction of the kidney.
It is a very rare infection nowadays, which must be considered in the event of persistent urinary disorders, of "cystitis" resistant to usual treatment, of the persistent presence of white blood cells in the urine without the presence of germs (leukocyturia without germs).
Above all affects young, immunocompromised adults in the absence of BCG vaccination, or in the event of a history of tuberculosis.
The diagnosis is made by demonstrating the bacillus in the urine, x-rays of the kidneys (appearance of the kidneys, ureters, bladder), cystoscopy and possible bladder biopsies.
The treatment combines several drugs for 6 to 10 months (isoniazid or INH, rifampicin, pyrazinamide), and sometimes requires surgical treatment (treatment of ureteral strictures, and in case of the small bladder). Undertreatment, the cure rate is 98% at 5 years.
Caused by a parasite, bilharzia (Schistosoma haematobium), the larvae of which enter humans via the skin when bathing in infested water (backwaters) in endemic regions (West Africa, etc.)
The disease is caused by the eggs being deposited in the tissues, the inflammatory reaction they elicit there, and the scarring of lesions which leads to fibrosis of the tissues.
The symptoms mainly combine urinary bleeding (hematuria) and urinary symptoms (frequent cravings, burning while urinating), and are all the more suggestive that they occur in a particular area: African patient from West Africa ( Mali, Senegal ...), but also patients who have been cooperating (agricultural work, military ...).
The serious forms are the result of reinfestations and mainly affect African patients affected from childhood.
The diagnosis is based on finding bilharzia eggs in the urine, and serology for bilharzia. Bladder or rectal biopsies are sometimes necessary
The medical treatment is very effective: praziquantel (Biltricideâ) with a single oral dose of 40 mg/kg. Surgical treatment only concerns the sequelae (ureteral obstruction, small bladder, etc.).
We deliver all over the world.
For more information, you can contact our experts on +229 51374202 direct line or by WhatsApp at the same number.